Dental sealants are a quick, easy, and relatively cheap (as opposed to the dentist bills you’ll accumulate for root canals) solution for preventing cavities. Although the idea behind sealants is not new, they’re quickly becoming the go-to treatment for kids who need extra help in the dental department.
“WHAT ARE DENTAL SEALANTS?”
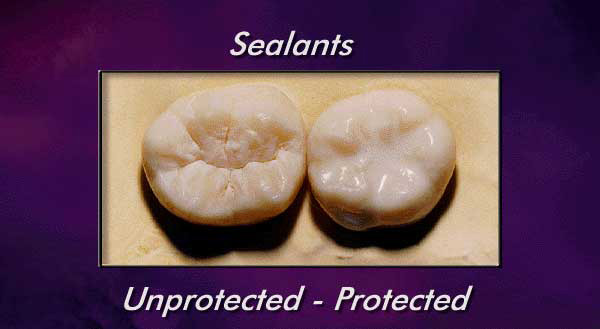
Sealants are a plastic material that is placed in the pits and fissures of the chewing surfaces of your teeth, particularly the molars at the back because toothbrushes can’t reach all the way into the grooves to clean well.
“WHO NEEDS DENTAL SEALANTS?”
Kids are notoriously bad brushers and tend to ignore the problem areas in the back of the mouth that lead to cavities and decay, making them the prime target market for sealants. (However, if adults have certain problem areas that could be cured with sealants, this could be an option for them too.) The American Dental Association recommends that kids receive dental sealants as soon as their adult teeth erupt.
Those who are more susceptible to cavities and decay – whether that is because they are genetically prone to cavities, don’t have great oral hygiene habits, or lack access to dental care – should consider getting dental sealants as a preventative measure.
“HOW DO DENTAL SEALANTS WORK?”
Dental sealants fill in and smooth out the grooves and fissures in your teeth that tend to hide food particles and attract cavity-causing bacteria. According to the American Dental Association, sealants work by “’sealing out’ food and plaque… [because] toothbrush bristles cannot reach all the way into the depressions and grooves.”
“HOW LONG DO DENTAL SEALANTS LAST?”
Dental sealants can protect the teeth for up to 10 years, but need to be checked frequently by a dentist for cracks. If dental sealants are worn down, it’s possible for decay to get under the sealant.
“ARE DENTAL SEALANTS EFFECTIVE?”
Dental sealants have been shown to reduce the risk of cavities in the teeth that are covered. According to Jonathan Shenkin, a spokesman for the American Dental Association, decades of research demonstrate that coating the biting surface of 6-year molars with a resin-based sealant can reduce cavities by up to nearly 80% immediately, and up to 60% for four years or more.
“WHY DON’T ALL CHILDREN GET DENTAL SEALANTS?”
The American Dental Association recommends that kids receive dental sealants as soon as their adult teeth erupt, but less than 40% of dentists actually comply. Studies by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention found that only 20% of children at poverty level and 40% of kids from higher income homes actually get the sealants.
A spokesman for the ADA and dentist himself, Jonathan Shenkin, said, “The lack of dentists doing sealants is a very silent, and probably the most significant, issue to care we face among children. Parents should be asking for sealants and not taking no for an answer.”
So why are some parents still slow to punch? There’s been a lot of debate over the effectiveness and safety of dental sealants.
“ARE DENTAL SEALANTS SAFE?”
If you’re a parent, you’ve probably heard the buzzword “BPA” quite a few times in recent years. The biggest factor in the general safety of dental sealants is Bisphenol A, commonly referred to as BPA, which is a resin used in many types of plastics. There is some evidence that BPA can be harmful to a child’s health, but it’s not conclusive. This evidence cites BPA is a hormone disruptor and one study tied prenatal exposure to BPA with hyperactivity and anxiety in babies, especially girls. In July of 2013, the FDA banned BPA in baby bottles and children’s drinking cups.
Dental sealants themselves don’t contain BPA, but many of them contain compounds that turn into BPA when they come in contact with saliva. However, professionals claim that “the amount of exposure is extremely low” and can be reduced even further. By scrubbing and rinsing sealants after they are applied, 88% to 95% of the compounds that can turn into BPA are eliminated.
The jury is still out on this one, as some dentists say there isn’t enough BPA present to warrant any concern, while others maintain that you shouldn’t expose yourself to any level of BPA if possible.
The one thing they do agree on? If you do opt for dental sealants, make sure to talk to your dentist first about scrubbing and rinsing the sealants thoroughly once they’re applied.
“DO ALL DENTAL SEALANTS CONTAIN BPA?”
This question is a bit tricky. Manufacturers are not required to disclose all of the ingredients in their products, and many (somewhat falsely) claim to be BPA-free. Dental sealants are plastic made from monomers that are derived from BPA, including bis-GMA and bis-DMA. BPA itself is rarely used in dental sealants. So in this sense, they are BPA-free. However, once the sealants are worn down and exposed to saliva, BPA is created by a chemical reaction.
“HOW MUCH DO DENTAL SEALANTS COST?”
As with all medical and dental treatments, the cost can vary depending upon the provider and your insurance. Typically, cost is around $30 to $40 for each tooth and is covered by most dental insurance providers.

Comments are closed